Marine
LOW RESIN ABSORPTION
Renewable energy
ULTIMATE ENVIRONMENTAL RESISTANCE
Antennas & electronics
LOW ELECTROMAGNETIC RESISTANCE
Medical
HIGH QUALITY COMPOSITES
Automotive
INDUSTRIAL FOAM PROCESSING
Aerospace
LIGHTWEIGHT STRUCTURES
Sport & leisure
ULTIMATE STRENGTH AND FLEXIBILITY
What is ROHACELL®?
The high-end sandwich core material ROHACELL® PMI foams, produced by Evonik, are a worldwide unique type of polymer foam sheet that is above other producers due to its superior strength to weight ratio combined with high thermal performance and stability.
What is ROHACRYL®?
ROHACRYL® foams, produced by Evonik, are a very new type of acrylic chemistry, allowing high thermal processing up to 120°C, with a very small and closed cell structure assuring very low resin uptake. That results in your weight and cost saving of resin.
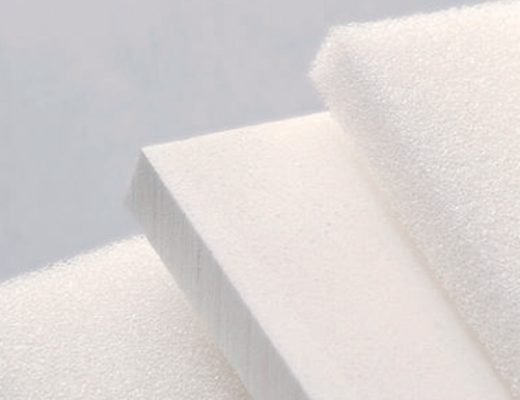

HIGH-PRECISION PRODUCTS
Why ROHACELL®?
- Excellent mechanical properties over a wide temperature range, even at low densities
- High temperature resistance up to 200°C
- Unique compressive creep behavior for processing up to 180°C and 0.7 Mpa
- Excellent dynamic strength
- Cell sizes that can be tailored for each processing method
- Excellent mechanical properties over a wide temperature range, even at low densities
- High temperature resistance up to 200°C
- Unique compressive creep behavior for processing up to 180°C and 0.7 Mpa
- Excellent dynamic strength
- Cell sizes that can be tailored for each processing method
HIGH VOLUME APPLICATIONS
Why ROHACRYL®?
- Recyclable structural foam for high volume applications
- High mechanical properties, whear modulus up to 47 MPa
- Very low resin uptake that equals even to 250 g/m2, that saves weight and lowers total raw material costs
- The superior thermal stability of Rohacryl with a value of 120°C make it possible to increase production speed
- Recyclable structural foam for high volume applications
- High mechanical properties, whear modulus up to 47 MPa
- Very low resin uptake that equals even to 250 g/m2, that saves weight and lowers total raw material costs
- The superior thermal stability of Rohacryl with a value of 120°C make it possible to increase production speed
OFFICIAL EVONIK DISTRIBUTOR AND PARTNER
What is CHEM-CRAFT?
CHEM-CRAFT is the leading supplier of ROHACELL® and ROHACRYL® foams in Nordic Europe, Eastern Europe and the BeNeLux countries.
Foams produced by EVONIK Operations GmbH provide impressive mechanical strength and creep compression strength, even at very low densities and a heat distortion temperature.
EVONIK high performance foams are mainly applied to composites industries such as automotive, sports and leisure, transportation, electronics, marine, renewable energy, aerospace and aircraft.
CHEM-CRAFT is the leading supplier of ROHACELL® and ROHACRYL® foams in Nordic Europe, Eastern Europe and the BeNeLux countries.
Foams produced by EVONIK Operations GmbH provide impressive mechanical strength and creep compression strength, even at very low densities and a heat distortion temperature.
EVONIK high performance foams are mainly applied to composites industries such as automotive, sports and leisure, transportation, electronics, marine, renewable energy, aerospace and aircraft.

CHOOSE A RELIABLE PARTNER
Why CHEM-CRAFT?
Chem-Craft consists of a team of composite engineers and experts that are specialized in composite processing methods such as: hand lay-up, RTM, infusion and autoclave. Therefore we have the know-how to distribute ROHACELL® and ROHACRYL® products offering also our suggestions and consulting advice.
Grades we offer:
- ROHACELL® 31 IG-F
- ROHACELL® 51 IG-F
- ROHACELL® 71 IG-F
- ROHACELL® 110 IG-F
- ROHACELL® 31 HF
- ROHACELL® 51 HF
- ROHACELL® 71 HF
- ROHACELL® 51 RIMA
- ROHACELL® 71 RIMA
- ROHACELL® 51 WF
- ROHACELL® 200 WF
- ROHACELL® 71 SL
- ROHACELL® 110 SL
- ROHACELL® 200 SL
- ROHACELL® 71 XT
- ROHACELL® 110 XT
- ROHACRYL® SW 60
- ROHACRYL® SW 80
- ROHACRYL® SW 100

Short lead time
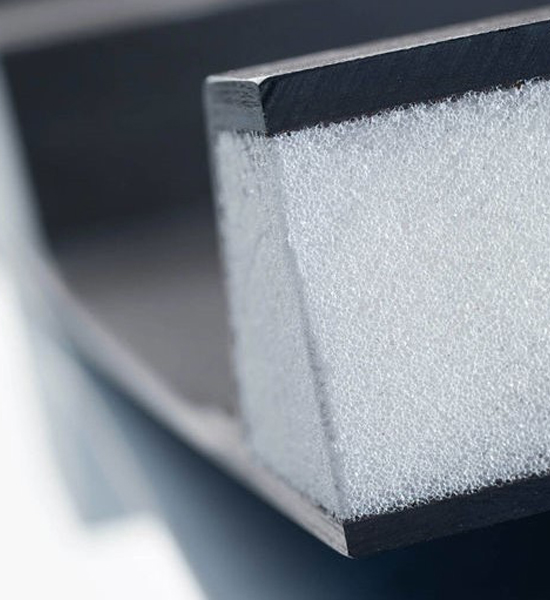

Low minimum order value
